Facts About Diamonds
Diamond Formation
Natural diamonds are mainly born in the high-temperature and high-pressure environment inside the earth. The pressure needs to reach 4.5 to 6Gpa and the temperature should be between 1100 and 1500 degrees Celsius, which is roughly equivalent to a depth of 150 to 200 kilometers underground. Under these extreme conditions, carbon atoms are packed tightly together and crystallize to form diamonds. From the diamond mines that have been explored, the vast majority of diamonds were formed billions of years ago, dating back between 2 to 3 billion years. Some diamonds discovered in South Africa are estimated to be around 4.5 billion years old, indicating that diamonds began crystallizing within the Earth shortly after its formation.
In addition to the natural formation inside the earth, modern laboratories or factories can quickly grow diamonds by simulating the growth environment of natural diamonds. The physical and chemical properties of the grown diamonds are exactly the same as natural diamonds.
Diamond’s Unique Physical and Chemical Properties
Diamond has the highest refractive index of all colorless gemstones, 2.417. This high refractive index causes light to converge towards the center of the diamond, producing eye-catching brilliance and fire. When light passes through a diamond, it is broken down into a spectrum of colors from red to purple, which is as brilliant as a rainbow. This is one of the important reasons why diamonds are so sought after in the jewelry industry.
In terms of specific gravity, diamond has a specific gravity of 3.52 grams per cubic centimeter, and its atoms are more tightly packed than ordinary gemstones. In some high-precision industrial manufacturing, diamond’s stable specific gravity can ensure its performance in specific environments.
Diamond is also the substance with the strongest thermal conductivity among known substances, with a thermal conductivity of 7 – 25 W/℃·cm, which is even better than the thermal conductivity of silver. This property makes diamonds widely used in the aviation industry and microelectronics industry. In the manufacturing of aerospace engines, diamonds can be used to make heat dissipation components, which can efficiently conduct heat away and ensure the stable operation of the engine; in the field of microelectronics, diamonds are used as radiator raw materials to help protect electronic components from overheating damage. Improve the performance and reliability of electronic devices.
The thermal expansion rate of diamond is very low, only (0.4 – 4.8)×10⁻⁶ in the temperature range of 193K – 1200K. It will not cause obvious thermal expansion and contraction due to temperature changes, which makes it suitable for various complex environments. It provides favorable conditions for the following applications.
Diamond Applications
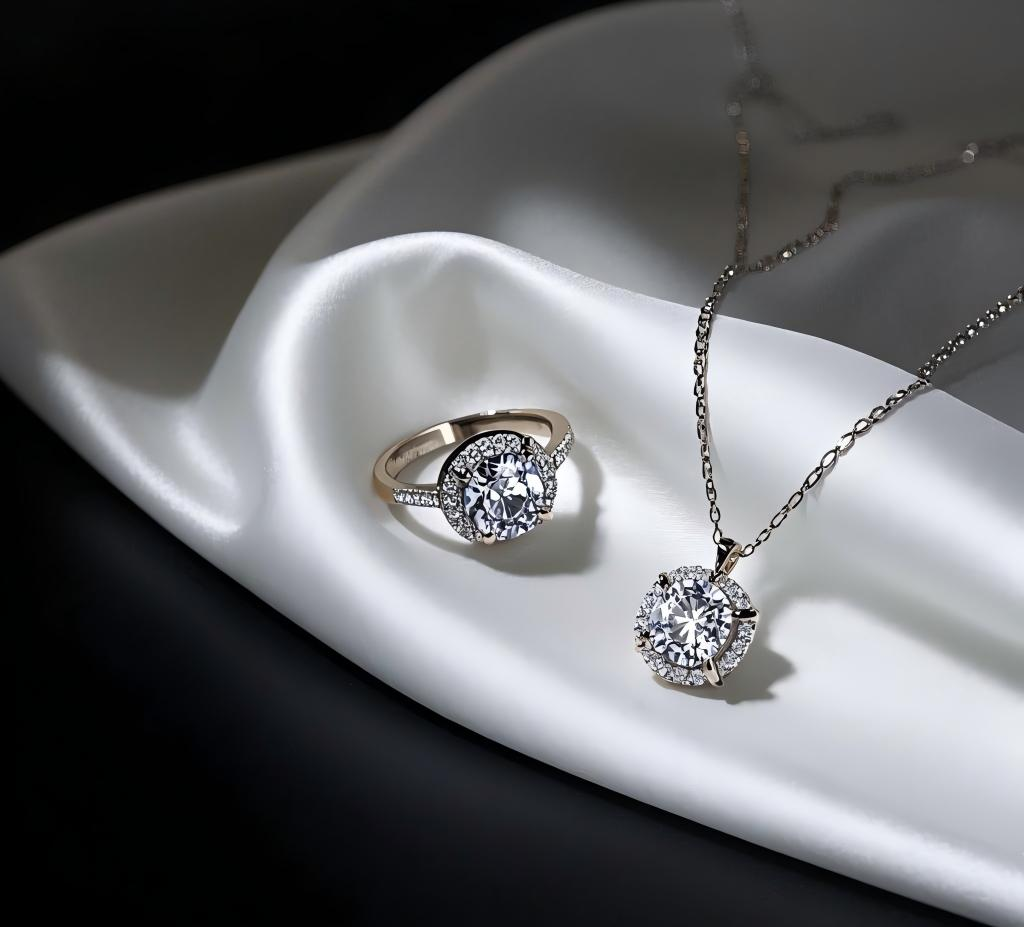
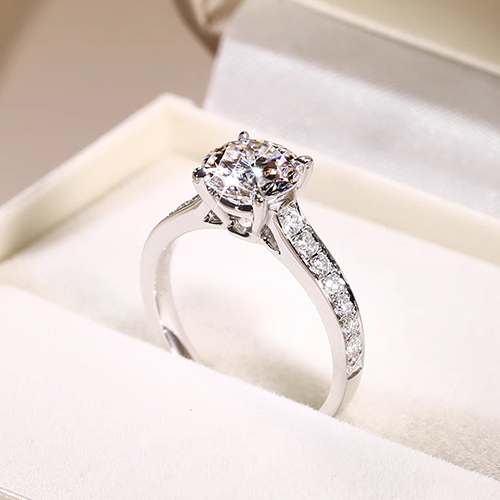
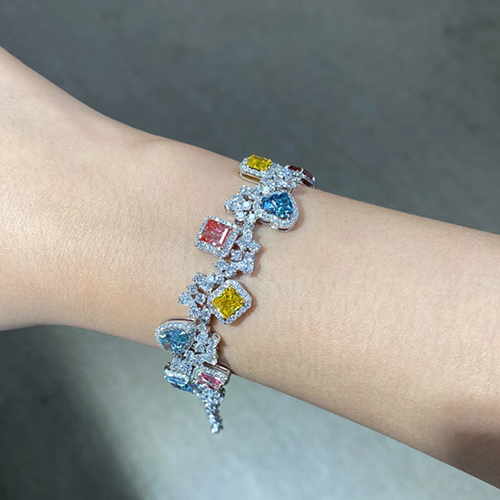
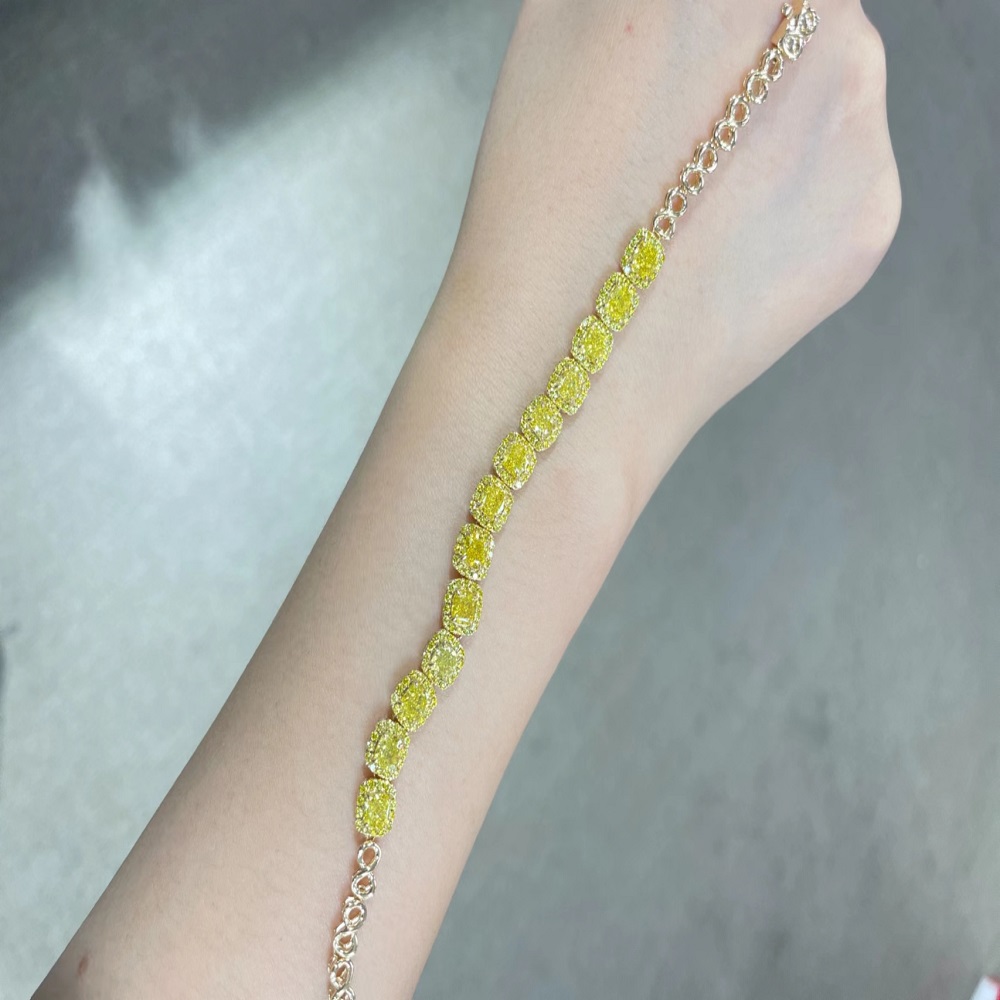
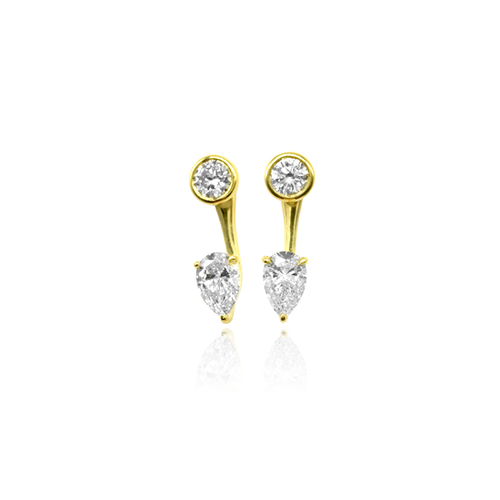
Diamonds have a wide range of applications, with jewelry being their most dazzling domain. From luxurious diamond rings and elegant necklaces to exquisite earrings and bracelets, diamonds captivate with their brilliance and timeless nature, making them a symbol of love, luxury, and refined taste.
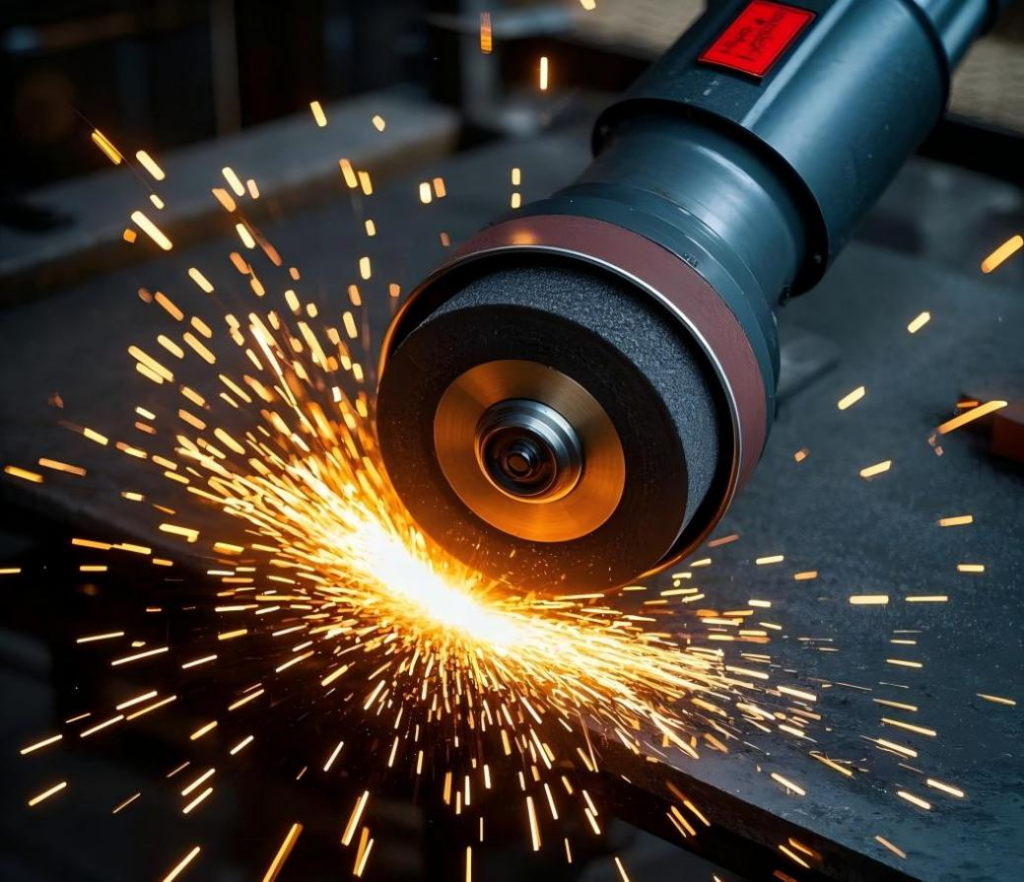
In the industrial field, diamonds also play an irreplaceable key role and a powerful assistant in the manufacturing industry. Due to its extremely high hardness, diamond is widely used in the manufacture of various cutting, grinding and drilling tools. For example, diamond drill bits can easily penetrate hard rock layers, greatly improving the drilling efficiency of geological exploration and oil extraction; in mechanical processing, diamond tools can achieve extremely fine cutting, effectively improving the accuracy and quality of products. In addition, diamonds can also be used to make abrasive tools such as grinding wheels and grinding pens. CVD diamond coating can enhance the durability and cutting efficiency of these tools. In the electronics industry, diamonds serve as ultra-wide bandgap semiconductors with exceptional physical properties. While their electrical performance still requires further refinement, they are already used in heat sinks and semiconductor materials. With their outstanding thermal conductivity and durability, diamonds hold great potential for future advancements in electronic devices.
Diamonds are particularly useful in the high-tech industry. In the field of microelectronics, it can be used for the polishing of modern super-strong materials; in laser equipment, it can create diamond anvils for high-voltage research and optical windows for high-power lasers; in the semiconductor industry, its unique properties help develop temperature , UV, X-ray and radiation sensors, etc.
Diamonds also have important applications in other industries such as medical care. With good biocompatibility and stability, diamonds are used to manufacture some high-end medical devices, such as coatings for artificial joints, components of pacemakers, etc., which helps extend the service life of medical devices and improve their performance.
The Impact of Lab Grown Diamonds on Natural Diamonds
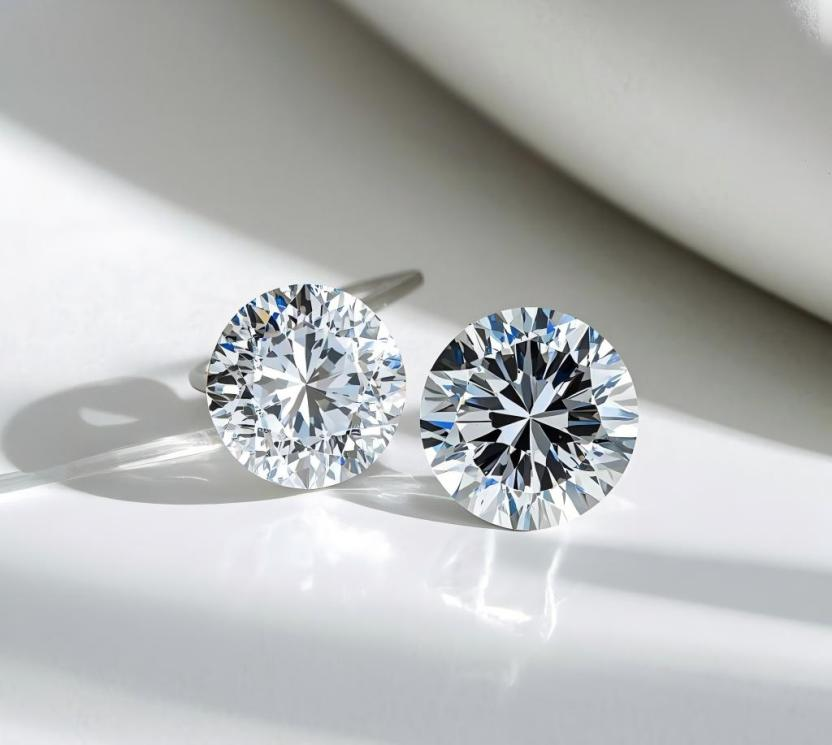
The emergence of lab grown diamonds has had a huge impact on the natural diamond market. Lab grown diamonds refer to diamonds synthesized in laboratories or factories. Their composition, appearance, structure and physical and chemical properties are exactly the same as natural diamonds. Professionals can distinguish between lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds with the help of equipment, but they cannot directly judge with the naked eye. Lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds are also subject to the 4C standards, and their various indicators are directly comparable.
The development history of lab grown diamonds is relatively short, but the development speed is amazing. With the continuous advancement of production technology, the quality of lab grown diamonds has continued to improve, and their market share has gradually expanded. According to data analysis by consulting firm Bain, China’s rough lab grown diamond sales in 2021 will be 1.4 million carats, and the lab grown diamond market penetration rate will reach 6.7%. It is expected that by 2025, China’s rough lab grown diamond sales will reach 4 million carats, and the lab grown diamond market penetration rate will reach 13.8%. In terms of price, lab grown diamonds have obvious advantages. The market price of lab grown diamonds of the same size and grade is much lower than the market price of natural diamonds.
As a precious gemstone, diamonds have always played an important role in human history. It not only has extremely high economic value, but also carries rich cultural connotation and emotional significance. However, with the changes of the times and the development of technology, the diamond industry is also facing many challenges and opportunities, which has also prompted industry giants to continuously adjust their strategies to deal with this unprecedented crisis. But no matter how the market changes, the bond between diamonds and humans has never diminished. In the jewelry industry, diamonds symbolize love and luxury, shining in life’s most precious moments. In industrial and emerging fields, their exceptional physical properties make them a valuable asset for technological advancements. Diamonds also play an irreplaceable role in mechanical processing, electronics, quantum computing, and many other industries.
Diamonds are not only beautiful treasures given to mankind by the earth, but also witnesses of mankind’s exploration of nature and pursuit of beauty. Its story will continue to shine through the years, leaving a unique and bright mark on the progress of human civilization.